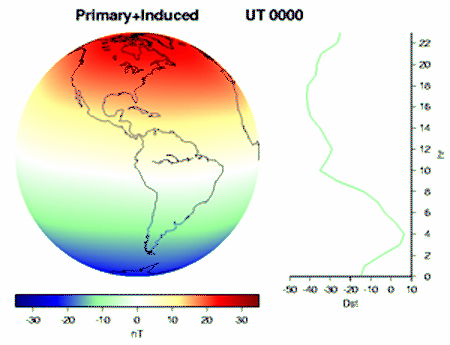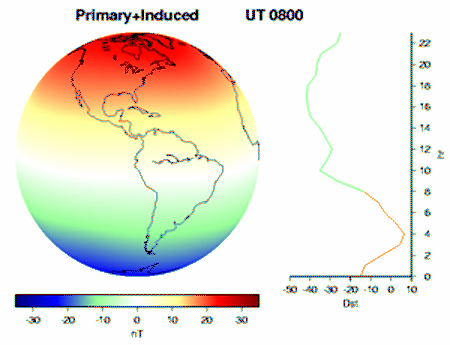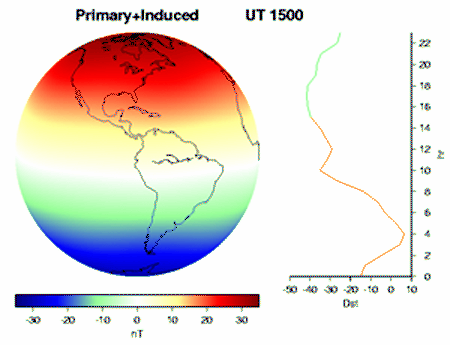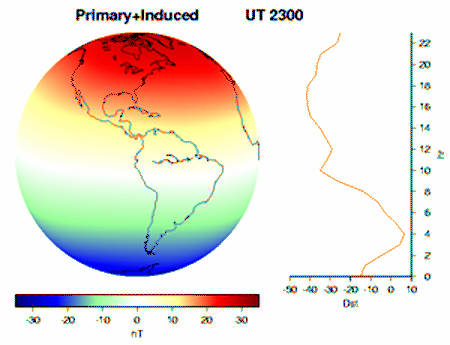
EARTH'S MAGNETOSPHERE
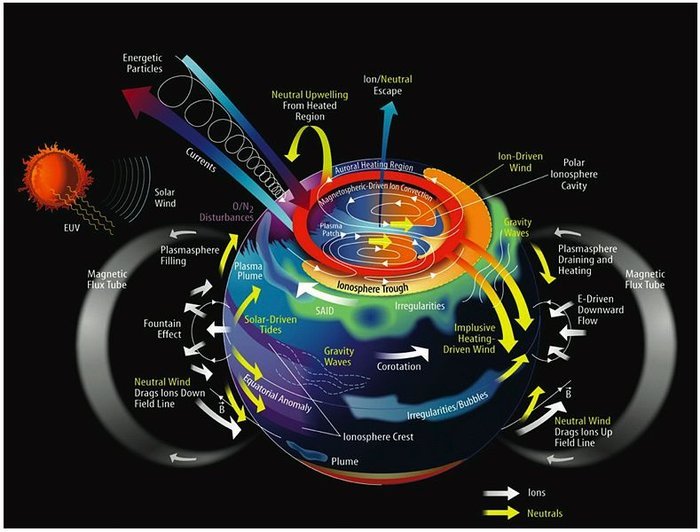
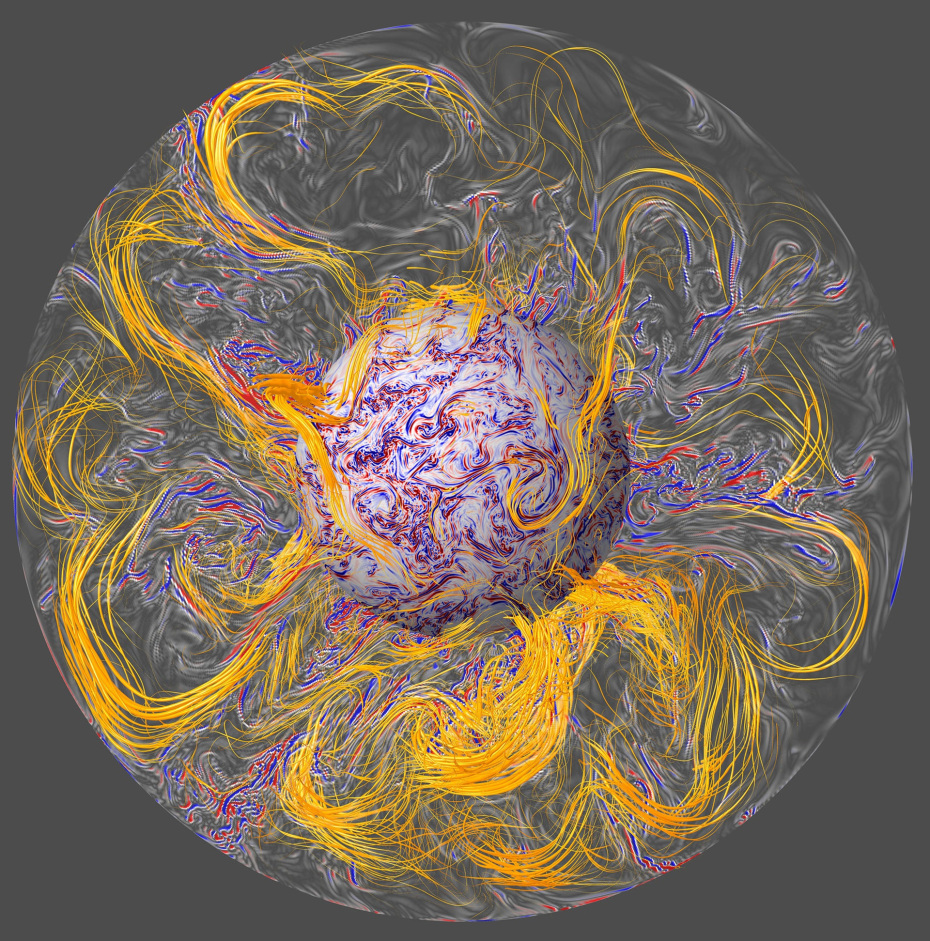
Plasma makes up 99.999% of the interplanetary, interstellar and intergalactic medium. The Sun is about 100% plasma, as are all stars. When solar mass ejections hit Earth’s ionosphere the ionized plasma gets discharged in touch with other noble gases and becomes visible in the night sky as Aurora Borealis
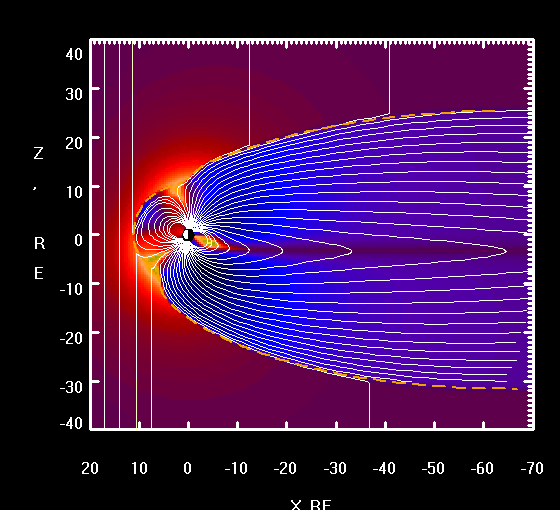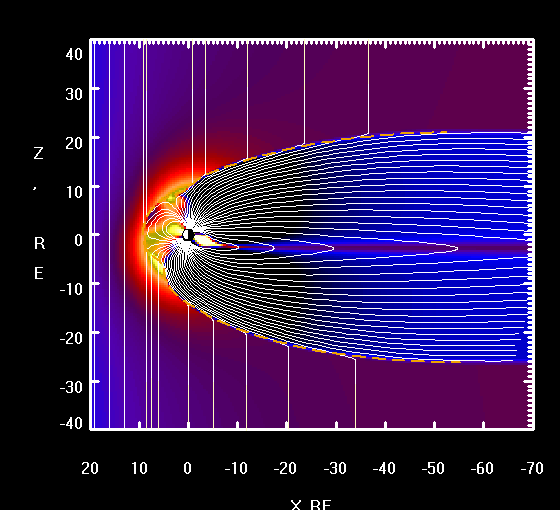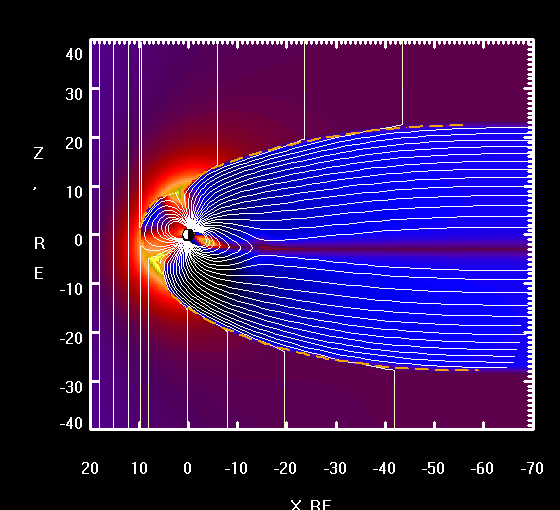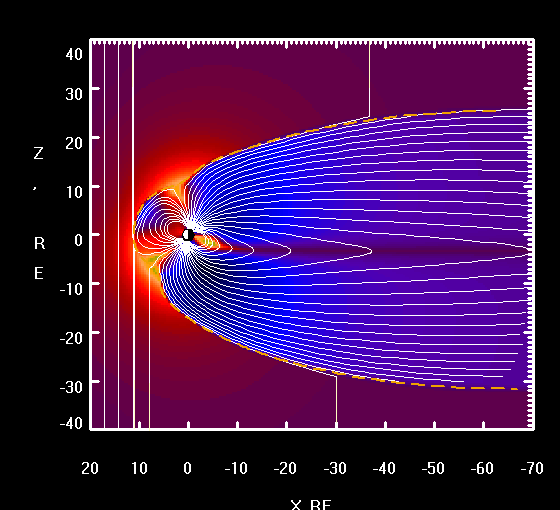
Solar wind consist of highly energetic particles, largly protons. During their approch they pass Earth's magnetosphere and induce a current whitin Earth's core known as dynamo effect. Parts of the particles get trapped in the regions called the Van-Allen-Belts where they block further incoming deadly radiation.
Dynamo Effect Accelerated by Solar Wind
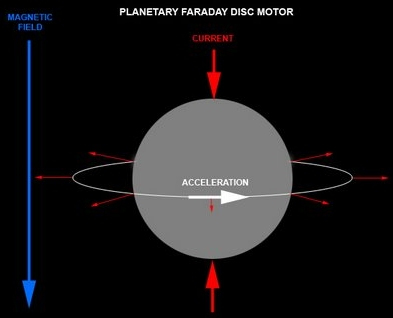
Rotation Induced by Hemispheric Discharge
Solar wind continuously induces current when passing trough Earth's magnetosphere. The Van Allen Belts store and the Hemispheric lobes absorb lots of these incomming protons. As Faraday's law of induction states, electric discharge such as consumed by the ionospheric polar and arctic jet streams results in rotation, as demonstrated by Faraday's disc motor. While Earth's outer iron core sinks to the center of least revolution and gets ejected at the cors furthest circumference, this conducts the negative counterpart of the circuit to the Hemispheres. Thus given, solar wind induces Earth's dynamo and keep it spinning, due to electrical discharge in the Earth's atmosphere, as well as its outer core.